Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignancies worldwide. It is characterized by poor prognosis and high mortality. The single-modality treatments, such as surgical resection, chemotherapy, external radiotherapy, and radio frequency ablation, show limited efficacy. So, there is a pressing need for multimodal therapies to improve therapeutic responses and prolong the survival of unresectable HCC patients. For example, the combination of chemotherapy and radiotherapy. But the effects are unsatisfactory for the radiotherapy and anticancer drugs do not simultaneously affect the same HCC regions.
Therefore, it is highly desired to employ an efficient radiosensitizer to enhance the response to radiotherapy, thereby providing a targeted strategy for exerting maximal synergistic chemoradio-therapeutic effect with minimal side effects.
Recently, Prof. DONG Wen-fei in Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology(SIBET), designed Janus-structured gold-mesoporous silica nanoparticles (GJNPs), which integrated chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and in vivo computed tomography (CT) imaging into a single system (Scheme 1). In this system, the folic acid (FA) on the surface of mesoporous silica was modified for HCC targeting, and the subsequent controlled release of the anticancer agent doxorubicin (DOX) was dependent upon acidic stimuli from the tumor microenvironment. The targeted delivery, selective cellular internalization, and pH-controlled drug release of FA-GSJNs-DOX NPs were assessed using hepatoma cell lines and normal liver cell lines with different FA expression levels.
The research revealed that the combination of chemotherapy and radiotherapy induced synergistic anticancer effects in vitro and exhibited remarkable inhibition of tumor growth in vivo along with significantly reduced systematic toxicity. Additionally, the Janus NPs acted as targeted computed tomography (CT)-imaging agents for HCC diagnosis.
Based on the better performance of Janus NPs in targeted chemoradiotherapy and CT imaging, this new nanoplatform designed with dual functionalities might be a promising platform for achieving efficient and safe HCC theranostics.
This research entitled “Janus Gold Nanoplatform for Synergetic Chemoradiotherapy and Computed Tomography Imaging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma” has been published in ACS Nano. (SCI, IF= 13.709)).
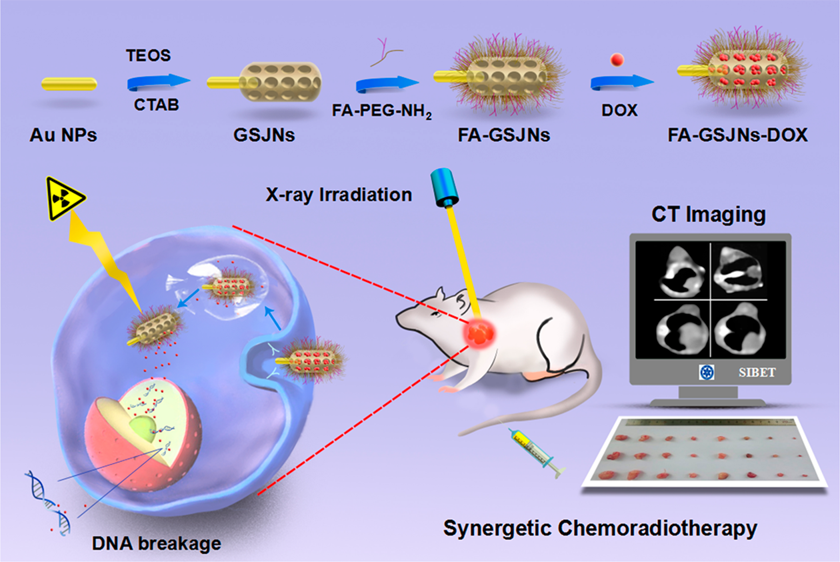
Scheme 1 Janus nanosystem might be a promising platform for achieving efficient and safe HCC theranostics.(Image by WANG Zheng)
Keywords: Janus Gold Nanoplatform; Synergetic therapy; Hepatocellular Carcinoma.
Contact
XIAO Xintong
Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (http://www.sibet.cas.cn/)
Phone: 86-512-69588013
E-mail: xiaoxt@sibet.ac.cn