In the treatment of liver cancer, radiation dosage constraints and hypoxia-associated resistance often lead to the failure of radiotherapy (RT). Photothermal therapy (PTT) has been considered as an ideal adjuvant therapy because of its controllable, facile, and noninvasive characteristics. More importantly, PTT partly ameliorates hypoxia by improving blood perfusion in tumor tissues, which facilitates radiosensitivity. Therefore, the intricate use of combined strategies for potentiating and complementing RT is especially important.
Recently, DONG Wenfei’s group in Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology of Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a new multifunctional platform, which was Janus-structured gold triangle-mesoporous silica nanoparticles (NPs). It can deliver the hypoxia-activated prodrug tirapazamine (TPZ) for improving extrinsic radiosensitization, local photothermal therapy, and hypoxia-specific chemotherapy.
The subsequent conjugation of folic acid linked poly (ethylene glycol) can provide the Janus nanoplatforms with liver cancer targeting and minimized opsonization properties.
In vitro and in vivo experiments revealed the combined radiosensitive and photothermal antitumor effects of the Janus nanoplatforms. Importantly, the TPZ-loaded Janus nanoplatforms exhibited pH-responsive release behavior, which effectively improved the cellular internalization and therapeutic efficiency in hypoxic rather than normoxic liver cancer cells. Hypoxia specific chemotherapy supplemented the ineffectiveness of radio-photothermal therapy in hypoxic tumor tissues, resulting in remarkable tumor growth inhibition without systematic toxicity. Therefore, the Janus nanoplatforms integrated radio-chemophotothermal therapy in a hypoxia-activated manner, providing an efficient and safe strategy for treating liver cancer.
This work entitled “Janus Gold Triangle-Mesoporous Silica Nanoplatforms for Hypoxia-Activated Radio-Chemo-Photothermal Therapy of Liver Cancer” has been published in ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces.
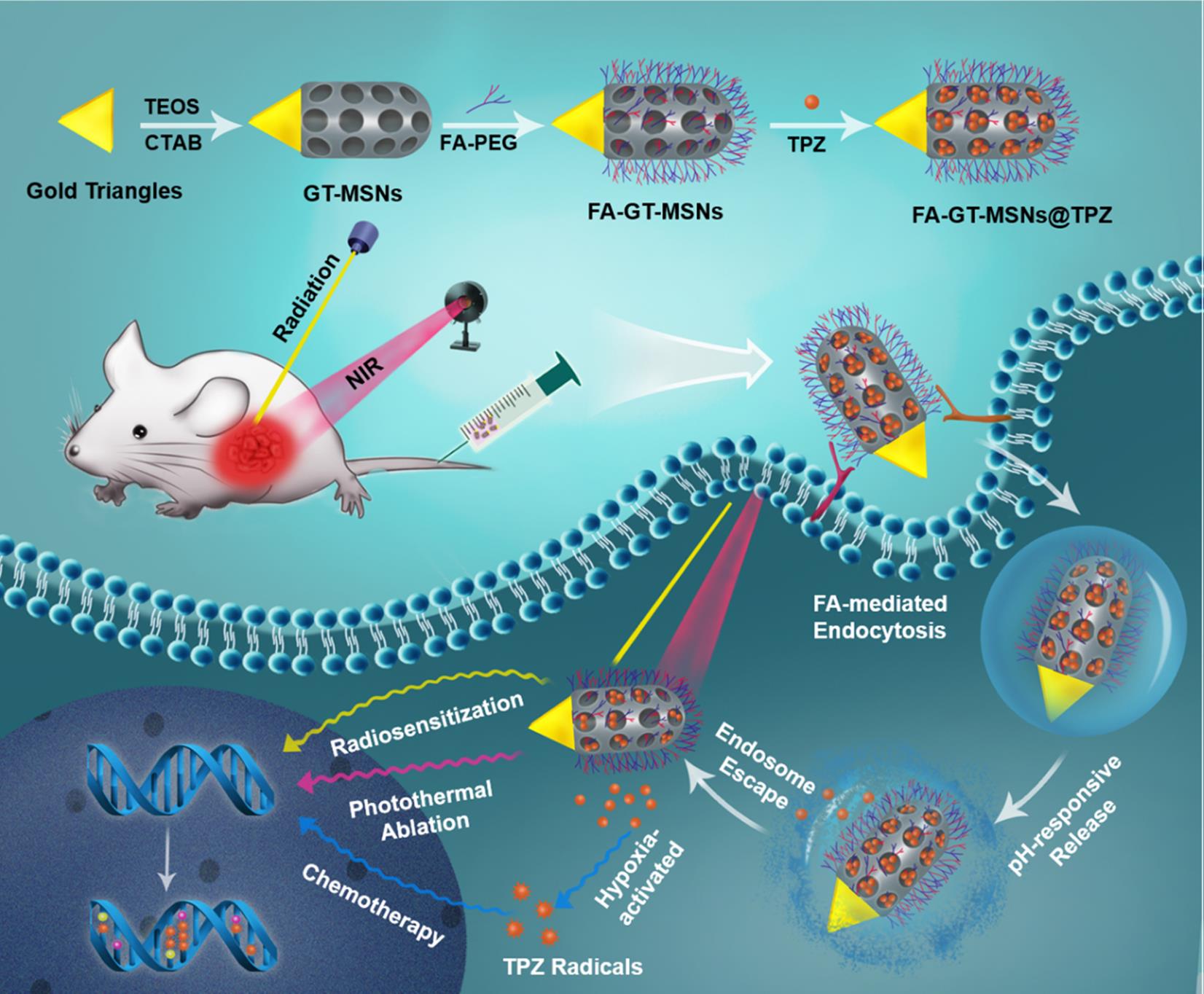
Figure 1. Fabrication of Janus Gold Triangle-Mesoporous Silica NPs (Janus NPs) with Liver Cancer-Targeting, pH Responsive Release, Hypoxia-Activated Chemotherapy, Radiosensitive and Photothermal Activities for Efficient and Safe Liver Cancer Therapy.(Image by WANG Zheng)
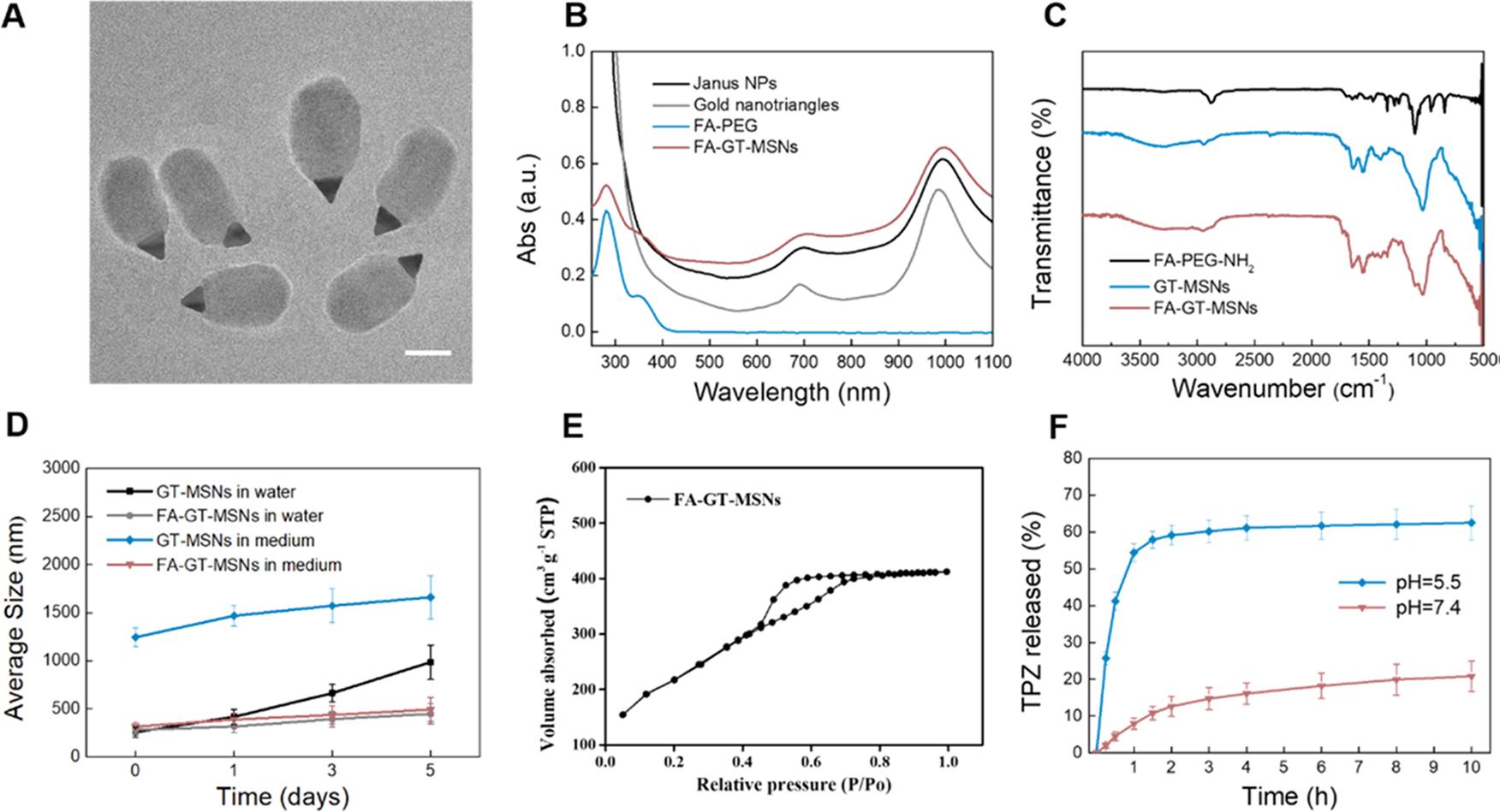
Figure 2 Characterization of FA-GT-MSNs. (A) TEM images (scale bar = 100 nm), (B) UV-vis-NIR spectra, (C) FTIR spectra of GT-MSNs, FA-PEG-NH2, and FA-GT-MSNs. (D) Average size of the GT-MSNs and FA-GT-MSNs in water and RPMI-1640 medium with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) for 1, 3, and 5 days. All of the data are presented as mean ± SD of three separate experiments. (E) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms of FA-GT-MSNs and (F) release behavior of TPZ from FA-GT-MSNs@TPZ at different pH values.(Image by WANG Zheng)
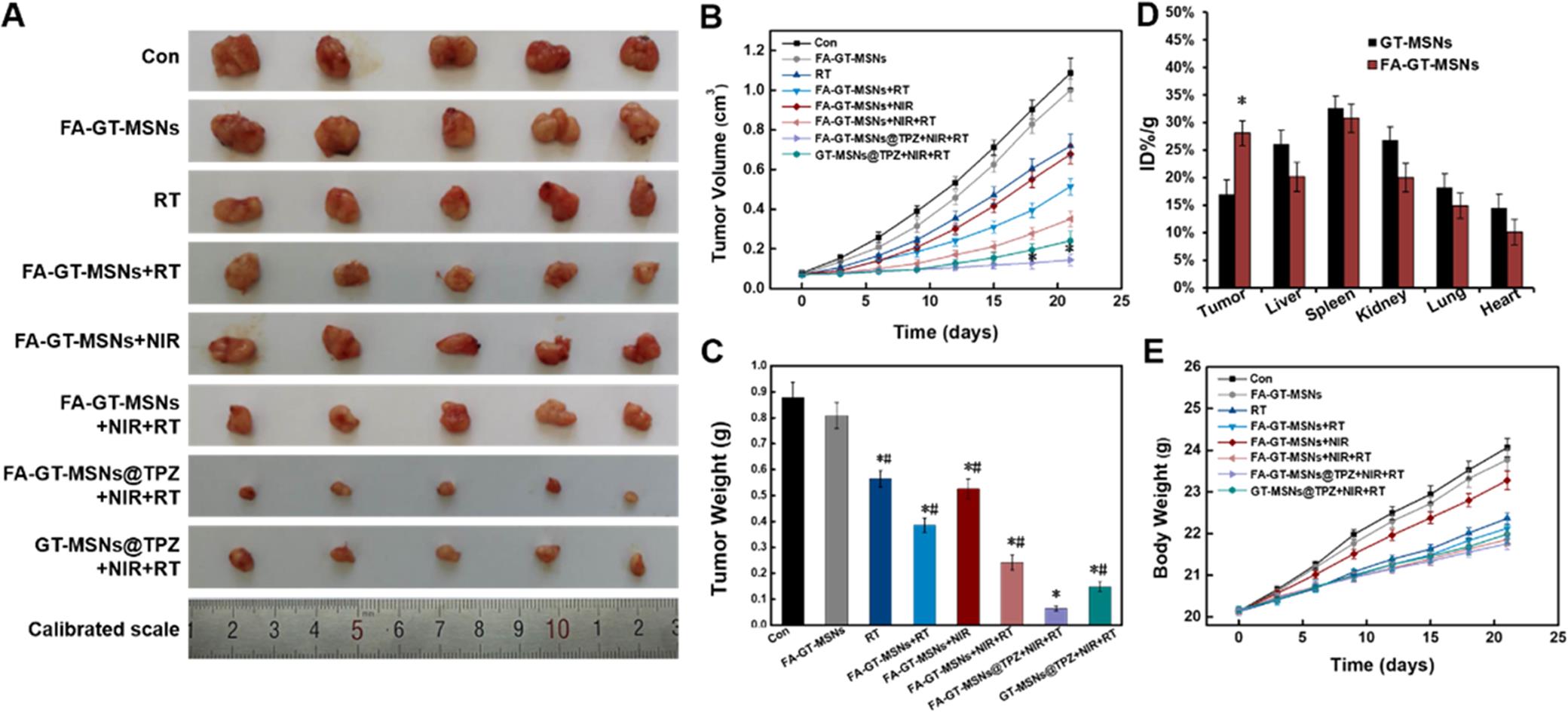
Figure 3. In vivo combined therapies. (A) Tumor images, (B) tumor growth curves, *p < 0.05 versus GT-MSNs@TPZ+RT+NIR groups. (C)Tumor weights from the mice in each group (n = 5), *p < 0.05 versus control groups; #p < 0.05 versus FA-GT-MSNs@TPZ+NIR+RT group. (D) Quantitative analysis of the accumulation of GT-MSNs@TPZ and FA-GT-MSNs@TPZ in the organs and tumors at 24 h post administration by ICP-OES, *p < 0.05 versus GT-MSNs group. (E) Body weights of the mice in each group. The values are presented as mean ± SD.(Image by WANG Zheng)
Contact
XIAO Xintong
Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (http://www.sibet.cas.cn/)
Phone: 86-512-69588013
E-mail: xiaoxt@sibet.ac.cn