Stretchable antenna has high potential in future wearable electronics with a low profile and integrated functions, however, their applications to strain sensing were limited due to their resonant frequency led by mechanical deformations.
Now, researchers may have a better solution to this limitation.
A group of researchers at Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology (SIBEBT) and Pennsylvania State University introduce arch-arranged mesh pattern stretchable microstrip antennas with a layered architecture.
On-body radiation efficiency of previous stretchable antennas may see severe degradation due to lossy human tissues.
The new proposed stretchable antenna, however, proves excellent on-body radiation performance with its varying 3D configurations.
“The stretchability of the antenna provides a nearly constant resonant frequency during deformation, enabling efficient on-body wireless communication,” said YANG Hongbo, one of the leading researchers from SIBEBT.
The stretchable 3D microstrip antennas showcase a strain-insensitive resonance, improved stretchability, and enhanced peak gain, compared to their 2D counterpart.
In particular, the optimized peak gain from the stretchable asymmetric 3D microstrip antenna allows it to transmit the energy and data wirelessly at an almost doubled distance. The transmission, in the meanwhile, enjoys as well as a doubled charging rate from the harvested RF energy.
The integration of stretchable antenna and rectenna with stretchable sensing and energy storage units can yield a standalone stretchable RF system for future health monitoring of humans and structures, according to the researchers.
The results from this work pave the way for the development of self-powered units with wireless transmission capabilities for stretchable body area networks and smart internet-of-things, said researchers.
The research papers “Strain-Insensitive Hierarchically Structured Stretchable Microstrip Antennas for Robust Wireless Communication” and “Standalone stretchable RF systems based on asymmetric 3D microstrip antennas with on-body wireless communication and energy harvesting” were published in Nano Micro Letters and Nano Energy.

Figure 1. Research results become journal covers. (Image by Nano Micro Letters)
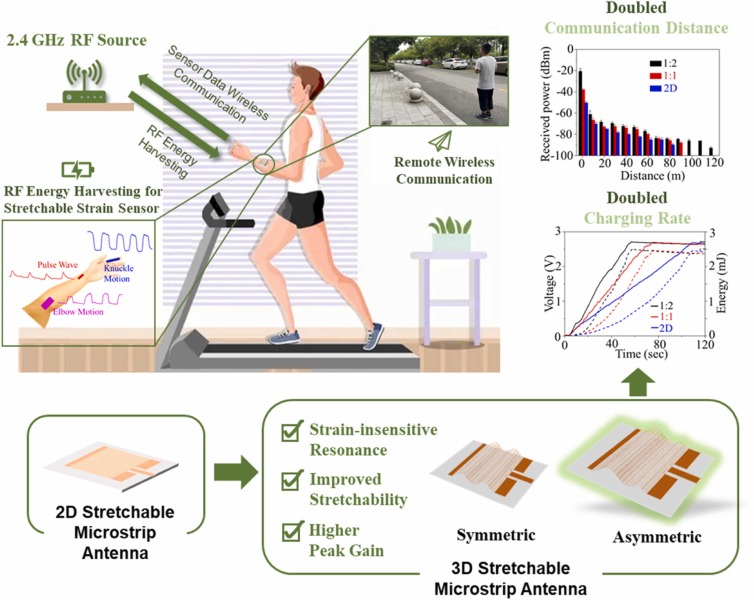
Figure 2. Design concepts of the standalone stretchable RF systems based on asymmetric 3D microstrip antennas with excellent on-body wireless communication and energy harvesting. (Image by SIBET)
Contact
XIAO Xintong
Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (http://www.sibet.cas.cn/)
Phone: 86-512-69588013
E-mail: xiaoxt@sibet.ac.cn