Fluorescence-activated droplet sorting technology (FADS) has become a powerful ultra-high throughput screening tool in the past decade. It is widely used in the screening of enzymes, metabolites and antibodies.
High-sensitivity fluorescence coupling strategy (FCSs) is a key technology for the application and development of FADS. It can couple enzyme activity, metabolite concentration, antibody affinity and other properties with fluorescence signals to achieve quantitative detection of target substances, which is one of the key links for the application and development of FADS.
Recently, a team of researchers from Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering Technology (SIBET) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reviewed latest research progress of fluorescence coupling droplet microfluidic of different analytical substances (enzymes, metabolites, antibodies) in the past decade.
They classified these strategies into four categories according to the principle of fluorescence coupling strategy: fluorogenic substrate strategy, enzyme-coupling strategy, biosensor-based strategy, and antibody-affinity-based strategy.
The review article was published on recent issue of Biotechnology Advances, entitled "Fluorescence coupling strategies in fluorescence-activated droplet sorting (FADS) for ultrahigh-throughput screening of enzymes, metabolites, and antibodies".
The research team, led by MA Fuqiang from SIBET, provided guideline for selecting the appropriate FCS for different analytes and matching the selected coupling system with a complementary FADS system. This offered an important complement for the existing review articles on FADS.
“The review provides an important theoretical basis for the application and expansion of droplet microfluidic system in enzyme, metabolite and antibody screening,” said MA.
The research was supported by the National Key R&D Plan, the National Natural Science Foundation, and the member funding plan of the Chinese Academy of Sciences Youth Innovation Promotion Association.
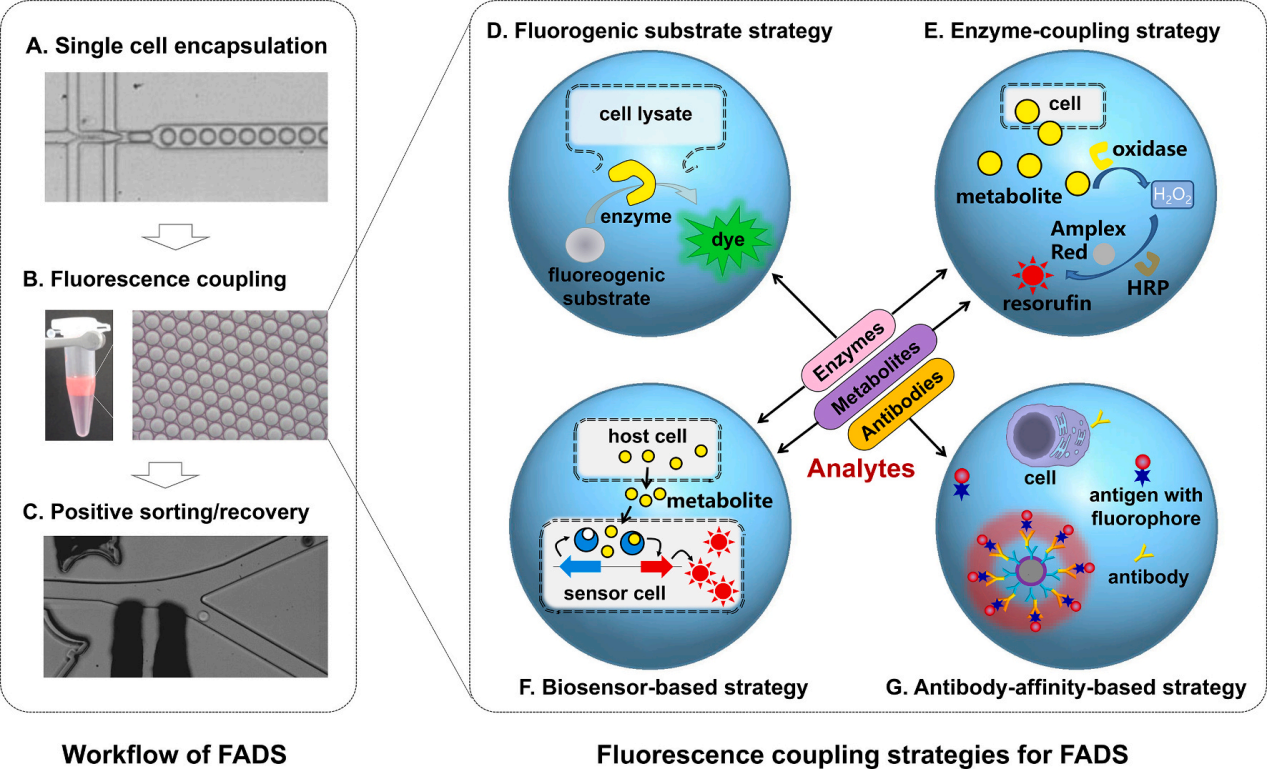
Figure 1. The work flow chart of FADS system is shown. (Image by SIBET)
Contact
XIAO Xintong
Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (http://www.sibet.cas.cn/)
Phone: 86-512-69588013
E-mail: xiaoxt@sibet.ac.cn