Lung cancer is the most common and deadly malignancy worldwide. Early diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer significantly increases the 5-year survival rate of patients. Bronchoscopy is the primary method for diagnosing and treating lung cancer. Traditional bronchoscopy has lower inspection efficiency. However, Electromagnetic Navigation Bronchoscope (ENB), which uses electromagnetic navigation technology and path-finding algorithms, can guide the bronchoscope in real time to quickly reach the lesion site for diagnosis and treatment. It is a novel technology that significantly improves the clinical efficiency of lung lesion diagnosis and treatment.
With the support of the Science Foundation of the Silk Road Project of the Office of the Vice President of Iran and the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the team of Dr. GAO Xin, Professor of Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology (SIBET) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the team of Dr. Alireza Ahmadian, Professor of Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Iran, jointly conducted the development of electromagnetic navigation bronchoscope. Both parties have jointly achieved a breakthrough in the key technology of ENB path search and proposed a novel path search algorithm.
A total of 50 cases of data from multiple centers were used for experimentation. The results showed that the algorithm exhibited superior path search performance, achieving an accuracy rate of 100%. Compared to the best-performing existing algorithm, the novel algorithm significantly reduced the average search time from minutes to seconds, a reduction of approximately 70%. In addition, the average memory consumption was reduced from gigabytes to megabytes, a reduction of approximately 80%. The new algorithm has the characteristics of high accuracy, fast speed, low memory consumption and strong generalization, which can greatly improve the performance of ENB, and has the advantages of easy deployment and popularization, and has a broad application prospect.
At present, the two teams have jointly developed a prototype of electromagnetic navigation bronchoscope principle, and successfully conducted model simulation experiments after using the new path search algorithm. They have jointly published seven high-level papers and obtained seven patents. In the future, they will focus on engineering prototype development and product optimization, conduct animal and clinical experiments, and try to obtain medical device registration. The transformation will be realized in both China and Iran, solving the problem of lung disease diagnosis and treatment, and benefiting the people of both countries.
In 2016, the vice president of science and technology of Iran came to China, visited SIBET. In recent years, the two sides have carried out cooperation through the construction of joint centers, exchange of researchers, projects and international conferences.
As the "Belt and Road Initiative" expands its "circle of friends", SIBET will also make greater contributions to the joint construction of the Belt and Road Initiative high-quality development, the service of the Belt and Road Initiative innovation road construction, and the realization of high-level bilateral international technology transfer and cross-border incubation.
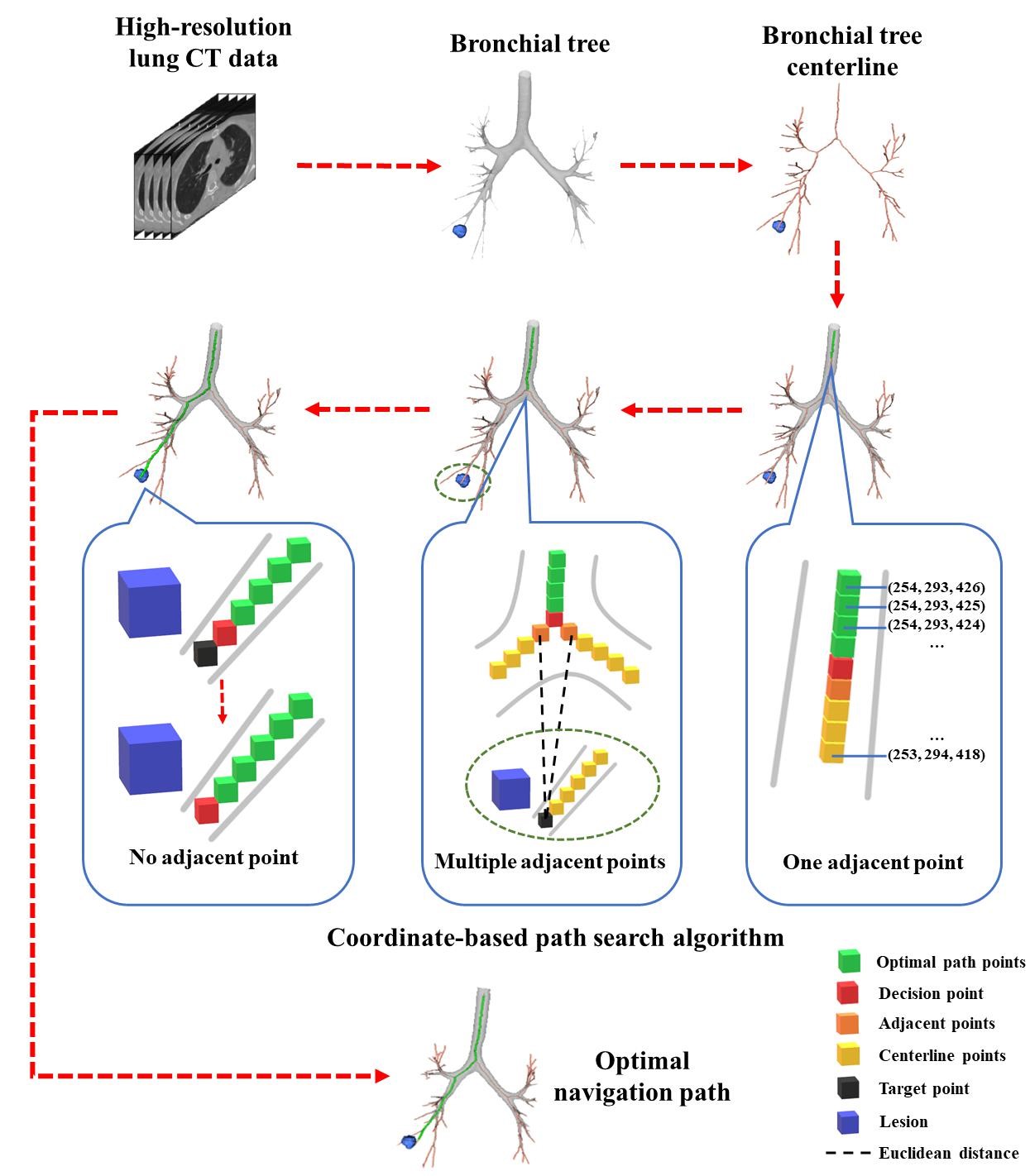
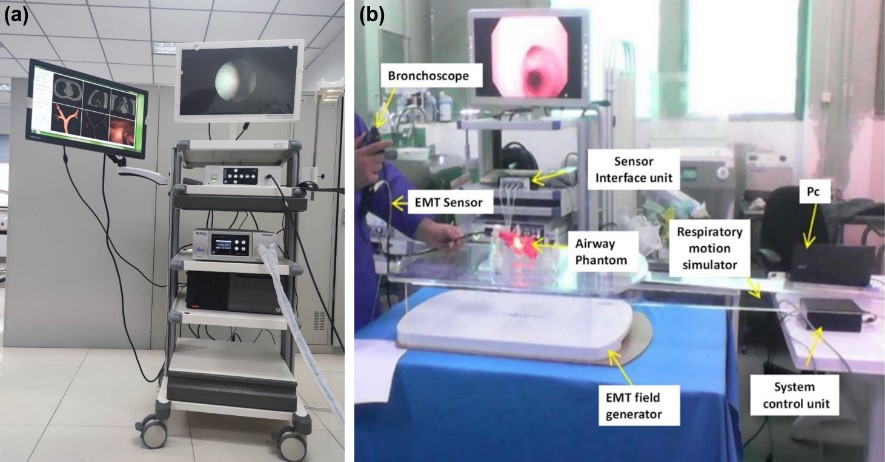
(https://english.cas.cn/Special_Reports/bricas/achievements/202309/t20230914_352598.shtml)