Modulation of T- cell mediated anti-tumor immune responses with monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) has achieved the brilliantly clinical success. Because of the innovative findings related to CTLA-4 and PD-1, which lead to the discovery of mAb-based immune checkpoint therapy, James Allison and Tasuku Honjo have been awarded the 2018 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
The activations of T- cells are balanced by co-stimulatory and co-inhibition molecules. T- cells are able to be released by inhibition of CTLA-4 and PD-1. Also there is another way to activate the T cells—— Refuel them!
Co-stimulatory molecules play pivotal roles in T- cell activation. 4-1BB (CD137, TNFRSF9), a member of TNFRSF, is a critical co-stimulatory checkpoint, which could inhibit T- cell apoptosis and regulate T- cell immune memory and differentiation. T- cells can be refueled by targeted 4-1BB.
Agonist mAbs targeting co-stimulatory 4-1BB, including urlumab (Bristol-Myers Squibb) and utomilumab (pfizer), have shown the promising efficacy in treatment of multiple tumors when combined with other immunotherapies.
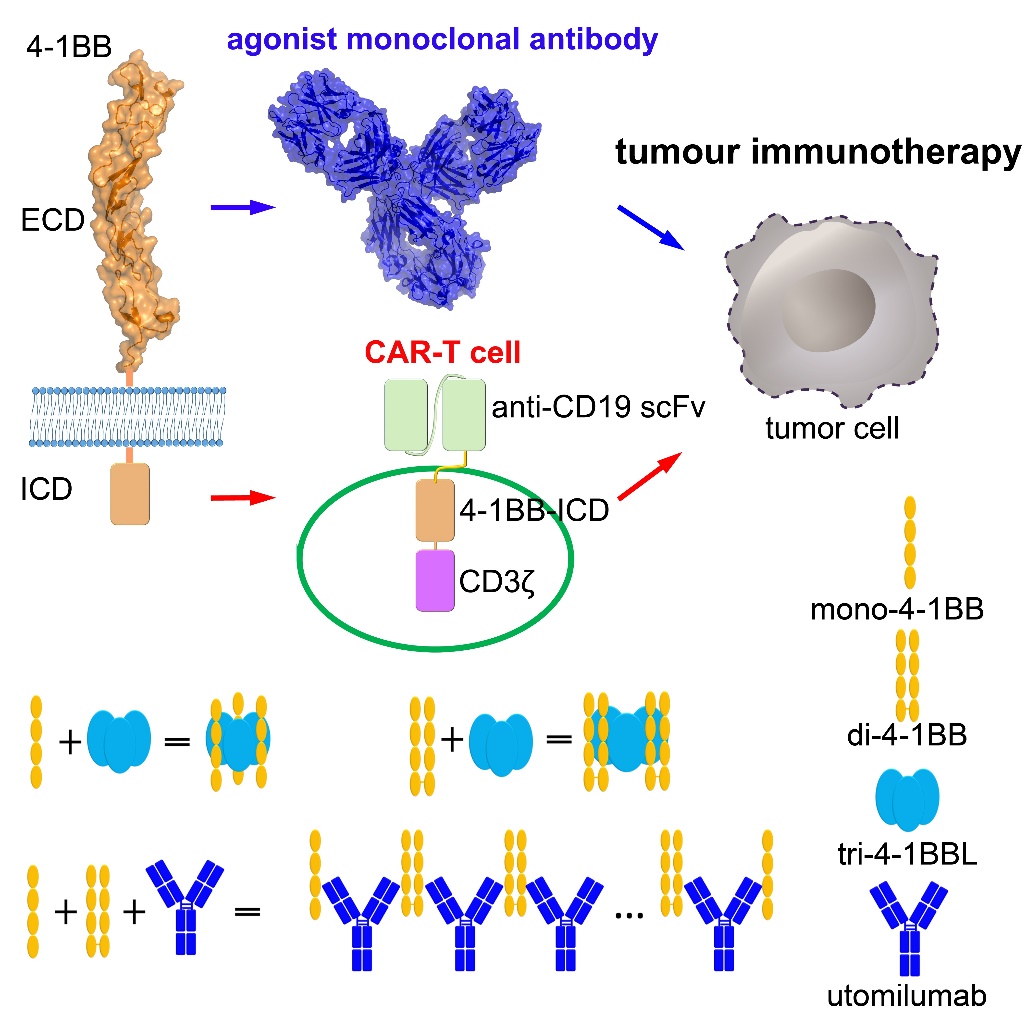
Figure 1. 4-1BB is a critical target for tumor immunotherapy. (Image by GAO Shan)
How do the antibodies work? Scientists from Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology (SIBET) and The Institute of Microbiology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IMCAS) dissected the molecular mechanism of antibodies.
When 4-1BB ligand (4-1BBL) and 4-1BB bind, they can co-stimulate the T- cells and refuel them. Based on that, scientists found that 4-1BB ligand (4-1BBL) and utomilumab were competitively binding to 4-1BB.
The complex structure of 4-1BBL/utomilumab shows that the binding surface of 4-1BBL and utomilumab for 4-1BB overlapped with each other. And this was further confirmed by both cell-based flow cytometry assay and protein-based Octet assays. The results show that the binding of utomilumab to 4-1BB have blocked the binding of 4-1BBL. So utomilumab can be used to bind to 4-1BB, which can refuel T- cells.
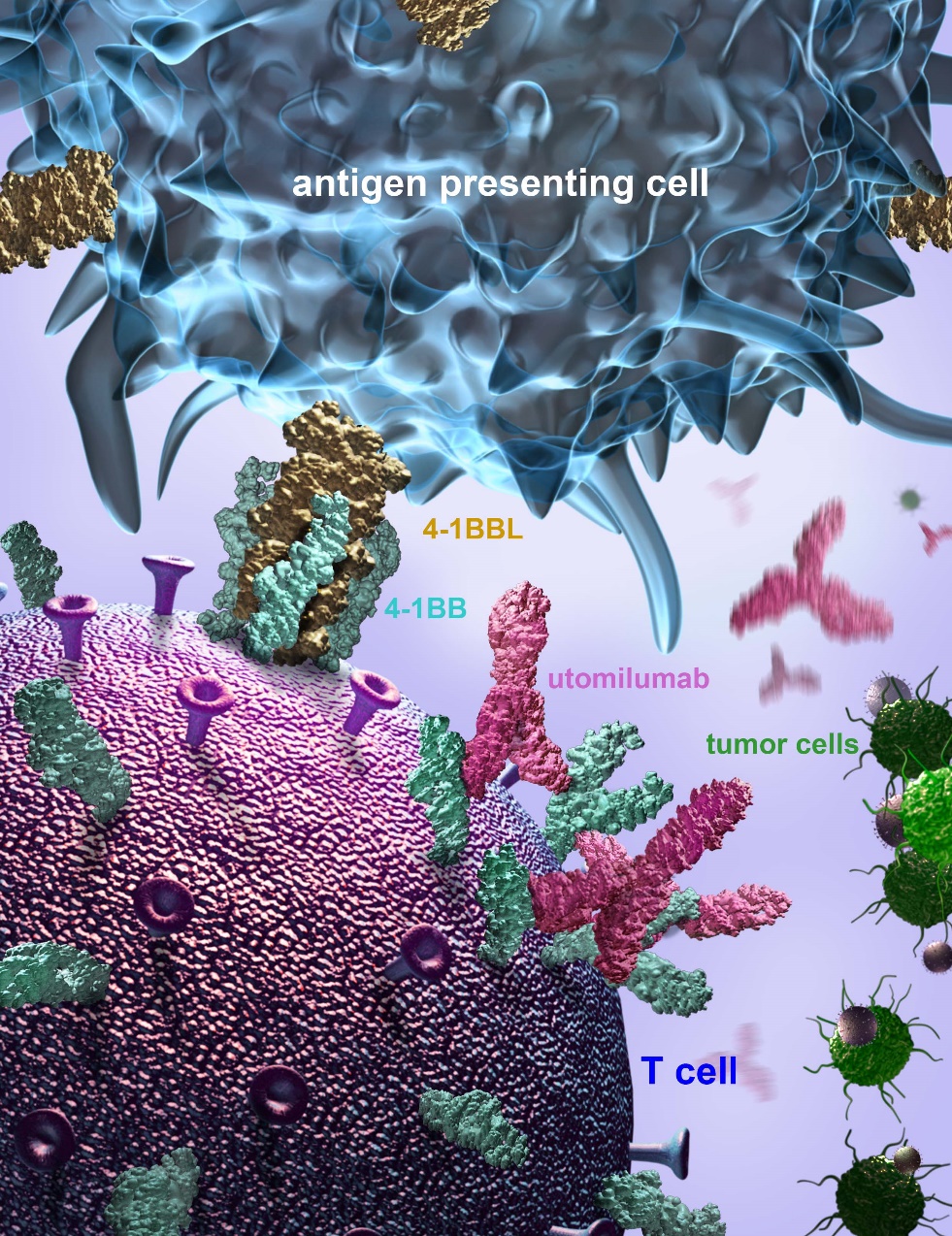
Figure 2. A model of 4-1BB binding to its ligand or utomilumab. (Image by GAO Shan)
Further study show that dimeric 4-1 BBS (di-4-1BB) has been found in human body and could be a new target. Both monomeric (mono-4-1BB) and di-4-1BB are detected to be expressed in activated T- cells. But di-4-1BB formation is only present in primates and some of the other mammals, suggesting that the presence of di-4-1BB might be correlated with immune system evolution.
The findings of the molecular basis of 4-1BB interaction with both its ligand and utomilumab would be useful for the development of biological agents targeting co-stimulatory 4-1BB for tumor immunotherapy.
The study entitled "Limited cross-linking of 4-1BB by 4-1BB ligand and the agonist monoclonal antibody utomilumab " was published in Cell Reports.
Keywords: immune; agonist antibody; utomilumab; 4-1BB.
Contact
XIAO Xintong
Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (http://www.sibet.cas.cn/)
Phone: 86-512-69588013
E-mail: xiaoxt@sibet.ac.cn