Heparin is commonly used in clinical medicine as anticoagulant. However, it tends to cause spontaneous bleeding and requires regular measurements during therapy. Potency detection is more meaningful than concentration detection in clinical diagnosis.
Recently, ZHENG Anran and ZHANG Wei from ZHOU Lianqun’s team of at Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology (SIBET) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, developed an enzyme-linked differential time sensor for heparin potency detection in whole blood.
The team established a novel heparinase-linked differential time (HLDT) method with a two-zone of graphene modified carbon (GR-C) sensor to evaluate heparin potency in whole blood. It was based on electrochemical measurement of clotting time shifting associated with presence or absence of heparinase.
Heparinase inhibits the anticoagulant ability of heparin by forming a heparin–antithrombin–thrombin complex during coagulation. And the intensity and peak time of electrochemical current were associated with thrombin activity and clotting on the electrode.
The results demonstrated that the heparin potency detection range of the GR-C sensor was 0.1–5 U/mL, its accuracy was 0.1 U/mL, and the coefficient of variation (CV) of the peak time was less than 5%.
"Thus, it provides better clinical application for the GR-C sensor with good repeatability, highly sensitivity and wide range,” said ZHOU.
Anticoagulation therapy is an effective treatment against thrombosis, it associated with the prevention and therapy of many thromboembolism diseases.
Clinical potency detection is not easily quantifiable and is limited in sensitivity. Most high-sensitivity heparin sensors have remained focused on the fluorescence method and measuring its concentration in clarified buffer solution.
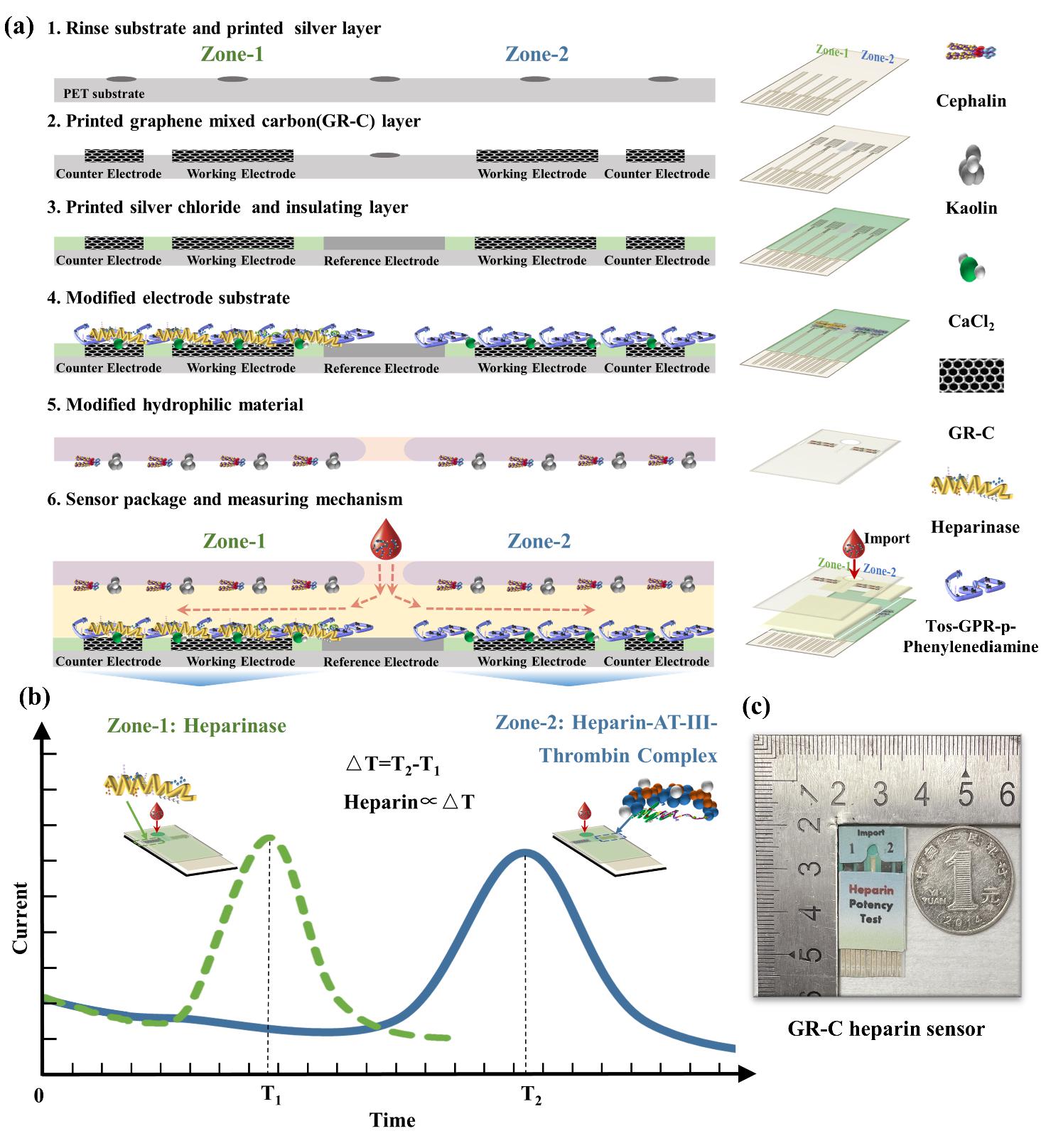
Fig. 1. Study of GR-C heparin sensor detection method: (a) Fabrication process of GR-C heparin sensor from 1 to 6. (b) Schematic of GR-C heparin sensor test curves. (c) Photograph of the GR-C heparin sensor. (Image by SIBET)
ZHOU's team has conducted in-depth research on coagulation mechanism and detection in recent years. They have proposed a series of original methods and new sensing technologies, and realized real-time monitoring of blood coagulation process.
They were able to accurately detect the coagulation time of plasma and whole blood samples, and made it possible for real-time monitoring of coagulation PT, APTT and other indicators with less sample volume and shorter detection time.
The team also developed coagulation point of care testing electrochemical detection sensor.
The development of coagulation miniaturization, real-time and rapid detection technology will be of great clinical value in the future in emergency, ICU, home medication and field rescue.
The research results, entitled "The heparinase-linked differential time method allows detection of heparin potency in whole blood with high sensitivity and HLDT method allows detection of heparin potency in whole blood with high sensitivity and dynamic range", was published in Biosensors and Bioelectronics.
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Key Research and Development Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology, the Major Research Instrument and Equipment Development Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Youth Innovation Promotion Council of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the Key Research and Development Program of Jiangsu Province.
Contact
XIAO Xintong
Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (http://www.sibet.cas.cn/)
Phone: 86-512-69588013
E-mail: xiaoxt@sibet.ac.cn