Point-of-care testing (POCT) devices show great advantages over conventional diagnostic tests, which are near patient settings and provide timely diagnostic information. Global POCT market has increased remarkably in the past decades. Distance-based devices are attracting great interest due to its simplicity, affordability, and ease of application.
Researchers at the Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology (SIBET) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences recently proposed a distance-based visual miRNA biosensor based on DNA hydrogels system (Figure 1).
The target miRNA-initiated strand displacement amplification process will produce abundant single-stranded DNA, which are essential probes for the linking of the three-way junction scaffold of hydrogel. Phase transition of the solution is confirmed by elastic and electrochemical techniques (Figure 2). A distance-based paper biosensing method is thus setup by establishing the relationship between the seepage flow distance along the strip and initial miRNA concentration (Figure 3).
Due to the strand displacement amplification, the biosensor is not only facile but also highly sensitive with a limit of detection down to 1 fM.
Since the three-dimensional DNA hydrogel affords abundant linking sites, the detection range is quite wide, according to the researchers.
The biosensor is demonstrated to be highly selective, and the results of human serum analysis are consistent with standard quantitative reverse transcription PCR.
“This approach exhibits the merits of convenient operation and low cost, meeting the requirements of point-of-care testing,” said Miao Peng, leading researcher of the study from SIBET. “It is promising as a convenient tool for miRNA-related biological studies and clinical diagnosis”.
Result of the study entitled “Distance-Based Visual miRNA Biosensor with Strand Displacement Amplification-Mediated DNA Hydrogel Assembly” was published in the recent issue of ACS Materials Lett.
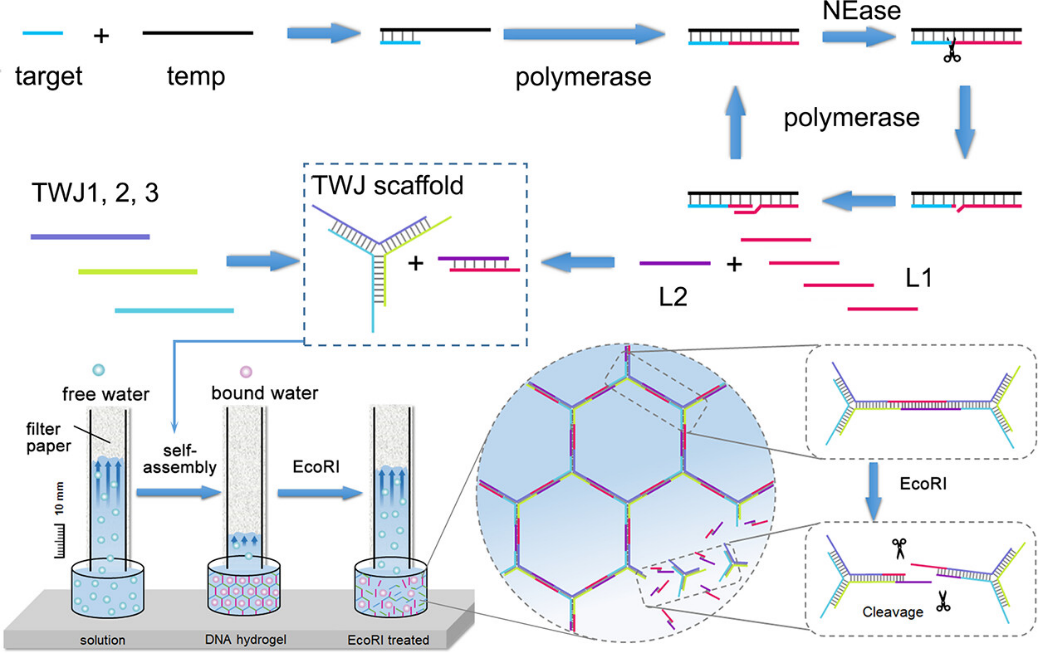
Figure 1. Illustration of the sensing principle of the distance-based miRNA assay. (Image by SIBET)
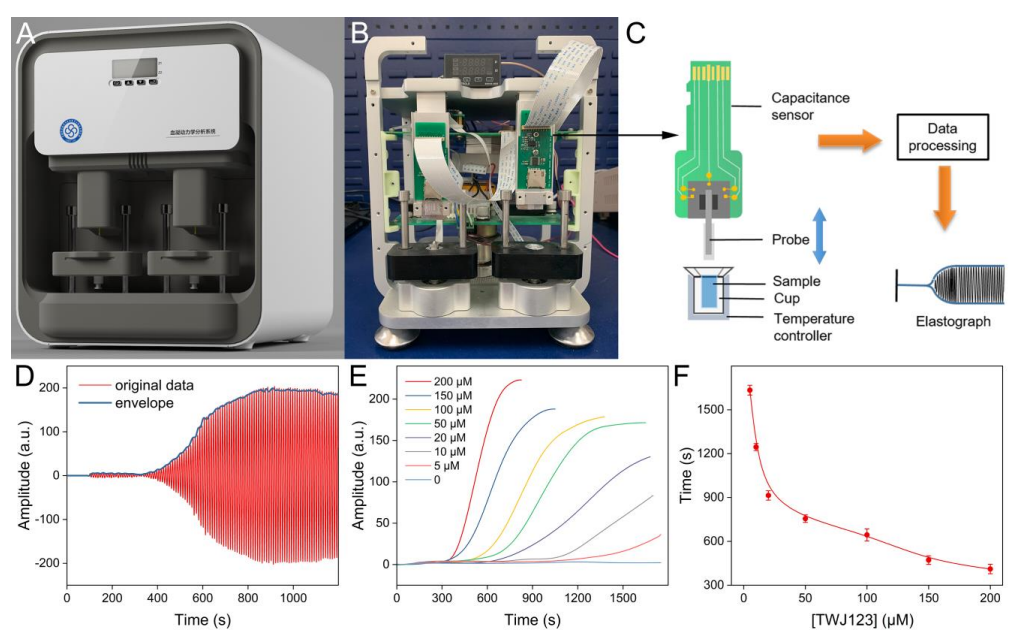
Figure 2. Principle of the elasticity instrument and the optimization by amplitude comparison. (Image by SIBET)
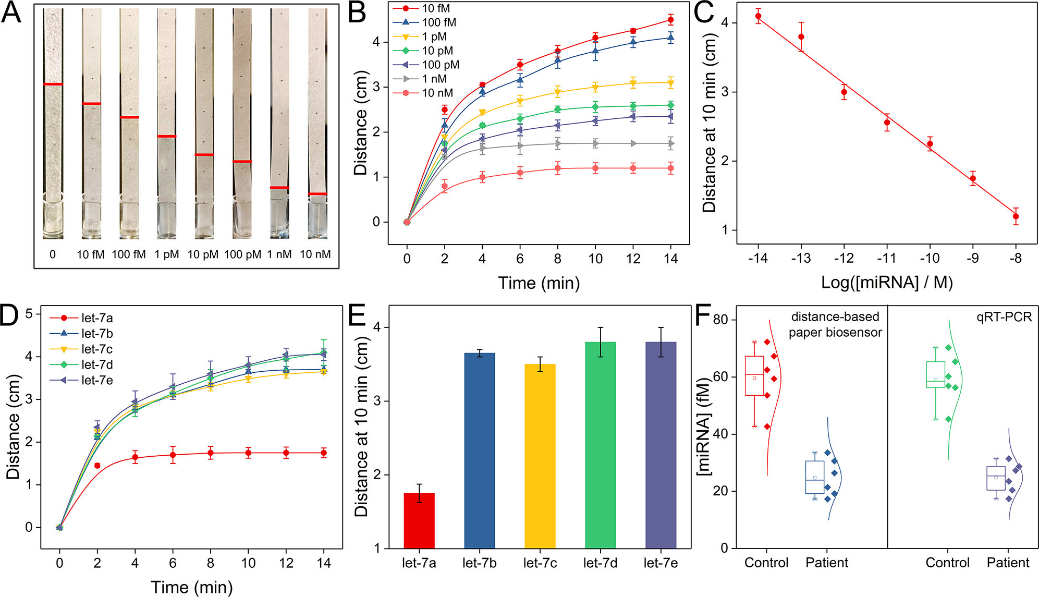
Figure 3. (A) Photograph of filter strips after the reactions with different amounts of miRNA. (B) Seepage flow distances of DNA hydrogel induced by miRNA. (C) Linear relationship. (D) Flow distances of DNA hydrogel induced by let-7a and the family members. (E) Comparison of the flow distances. (F) Concentrations of miRNA in control and patient samples. (Image by SIBET)
Contact
XIAO Xintong
Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (http://www.sibet.cas.cn/)
Phone: 86-512-69588013
E-mail: xiaoxt@sibet.ac.cn